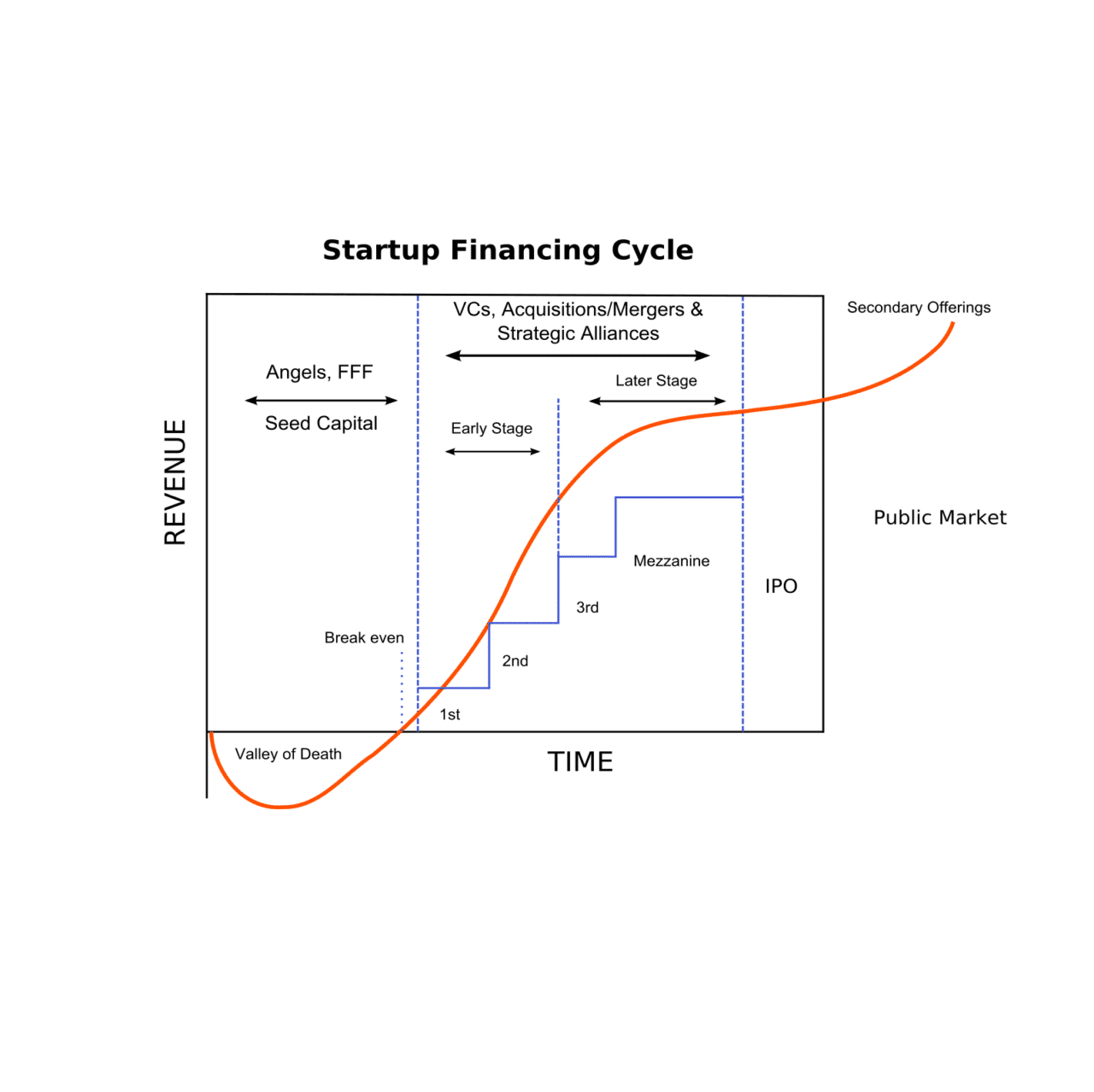
Venture capital investment is needed to raise third-party capital for a promising startup, financing rapid growth. The investment allows either the development of a new product/idea (early stage) or the rapid growth of an existing business (later stage/growth stage). Such investments are considered risky, but the risk of such projects justifies the expectation of super profits, which in the case of venture capital investment exceeds the amount invested many times over. To minimize risks and streamline investments, the process of financing a project through venture capital funds usually is divided into several stages.
The stages of venture round financing:
Seed funding
This is a very early investment, the first necessary stage to prove new ideas. Seed funding helps start-ups become fully operational. At his stage, the start-up company has a concept, an idea for a product, but no finished product. Investors can be venture capitalists, angel investors, accredited investors, equity crowdfunding investors, revenue-based financing lenders, or government programs.
Early stage
Investments for the early-stage companies having a pilot version of the product or the first version for demonstration; the product becomes tested. Typically, early-stage companies need funding for marketing and product development expenses.
- Series A round: Early sales and manufacturing funds. Investing in the market launch phase, setting-up mass production, and hiring a full team.
- Series B round: This round involves scaling up the company after reaching pre-determined targets. Often such a round fosters expanding into new markets, scaling up in an established niche, and increasing profits.
- Expansion or mezzanine financing (Series C round): Expansion money for a newly profitable company. The product has been accepted by the market and there has been a rapid increase in sales and demand.
Later stage (Series D round)
The company transforms itself into a large organization, showing the features of a public company.
Depending on the type of company, e.g. SaaS or Deep-Tech, both the number of rounds as well as the round designations will be different. A Deep-Tech startup will require substantially more rounds before becoming profitable, as compared to the average SaaS company (hence the preference for many of the VCs to invest in software rather than in hardware).
Image credits: Startup Financing Cycle By Kmuehmel